Pulmonary Embolism
by: Marianne Bird
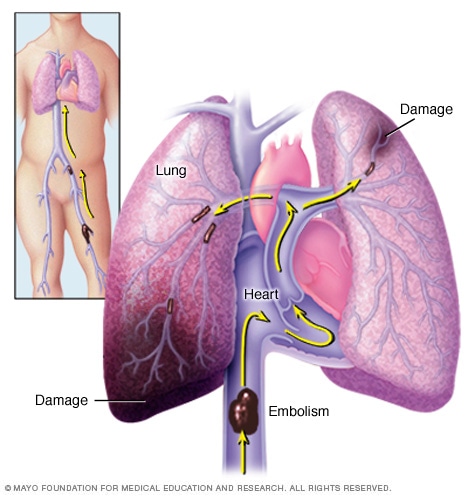
Pulmonary Embolism is a sudden blockage in the lungs, caused by a loose blood clot that breaks free and is pumped through the body and into the pulmonary artery where it lodges. This can be life threatening. It causes low oxygen levels in the blood stream, permanent lung damage as well as damage to the organs that are cut off from oxygen supply. Pulmonary Embolism is usually caused by a blood clot that forms in the leg, or rarely, from another part of the body, deep vein thrombosis. Pulmonary Embolism can be one large clot or several smaller clots. Sometimes there are no symptoms but shortness of breath, feeling of heat, redness or tenderness in the leg, coughing up blood can be indicators. Some typical risk factors are age over 40, prolonged bed rest or travel, surgery, those with preexisting medical conditions like cancer, heart or kidney disease, those who smoke cigarettes, take estrogen birth control or hormone therapy, family genetics or obesity.
Treatment for pulmonary embolism can be medicinal or procedural. Medicinal blood thinners called anticoagulants, can be given in pill form, injected or given intravenously. The blood thinners will prevent more clots from forming and keep existing clots from getting bigger but can cause bleeding. If the pulmonary embolism is very serous with large clots, thrombolytics, medicine that dissolves clots can be issued but can cause sudden bleeding and should be used only if the PE is life threatening. A filter can be surgically inserted into the vena cava, a large vein with access to the lungs. The vena cava filter will catch blood clots before they enter the lungs and can be a good option for those who cannot take blood thinners, but will not prevent future clots from forming. Anther procedure that is used is called catheter assisted thrombus removal. The patient is put under anesthesia and a tube is inserted with a tool inside to break up the clot or to issue medicine directly to the clot.
Pulmonary Embolism is one of the leading causes in preventable hospital deaths, 5-10% of deaths in hospitals are related to this. Studies suggest that one million people are effected by PE per year and out of that 100,000-200,000 are fatal. It is known as the silent killer because less than half of the people that die as a result of pulmonary embolism where diagnosed with it. About 31% of people discharged from hospitals are at risk of developing pulmonary embolism and half of all PE cases reported happen to those in hospitals or nursing homes. It costs about 10 times more to treat Pulmonary embolism than it does to prevent it.
works cited:
https://medlineplus.gov/pulmonaryembolism.html
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-embolism/symptoms-causes/syc-20354647?page=0&citems=10
https://www.thoracic.org/patients/patient-resources/breathing-in-america/resources/chapter-16-pulmonary-embolism.pdf
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.