Organ Histology of the Lung
by
Elisa Ruiz
Structure:
The conduction part of the lungs begins at the trachea and extends to the bronchioles. The conduction system consists of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx, larynx and trachea. The speicalized cells in the lung/ respiratory system warm, moisturize and remove particles that enter the lung. Respiratory epithelium is mostly made up of ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. There are 5 types of cells that that make up the tissues in the lung. They are ciliated cells, goblet cells, basal cells, brush cells and neuroendocrine cells. Each of these cells perform different functions to form the lung.
Function:
Ciliated cells are make up most of the lung tissue. It controls the defense mechanism that removes debris from our lungs. Goblet cells are filled with mucin and decrease as they reach the respiratory bronchioles. Basal cells help to attach layers of ciliated cells and goblet cells. Brush cells no functions have been specifically assigned to these cells but are thought to monitor air quality. the functions of the lung as an organ are respiration aka breathing and air conditioning which means cooling and heating the air we breathe to body temperature.
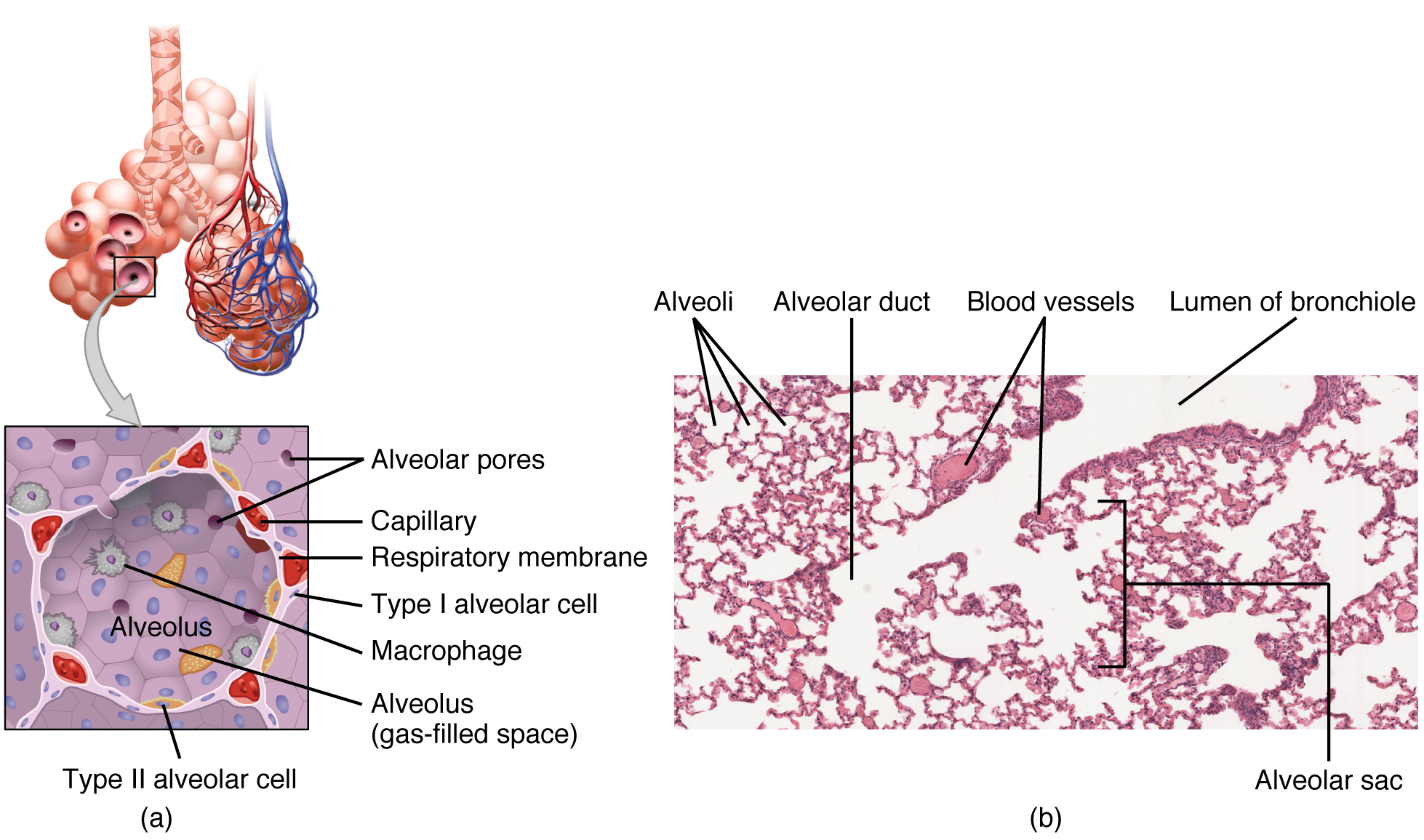
Photo URL:
https://opentextbc.ca/anatomyandphysiology/chapter/22-1-organs-and-structures-of-the-respiratory-system/
URL Sources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534789/
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.